Step into the exciting world of digital marketing, where using analytics and data-driven strategies is like adding magic to your plan.
This guide is your friendly companion, helping you understand how to make your marketing strategy way more exciting with the power of data. It doesn’t matter if you’re a pro or just starting – learn how to make the most of data to make your marketing stand out.
It’s not just about keeping up; it’s about making your marketing awesome with the magic touch of data. Welcome to a world where your marketing doesn’t just get better; it gets really cool!
What is Data Driven Marketing?
Data-driven marketing is an approach where decisions and strategies are based on insights derived from the analysis of various types of data. In simple terms, it involves using information and statistics about customer behaviour, preferences, and interactions to tailor marketing efforts for better targeting and effectiveness.
Rather than relying solely on intuition or generalized assumptions, data-driven marketing uses concrete data to guide decision-making. This data can come from various sources, including customer interactions with a website, social media engagement, purchase history, and more. Analyzing this data helps marketers understand their audience better, allowing them to create more personalized and relevant campaigns.
The key aspects of data-driven marketing include collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to inform marketing strategies. By understanding what works and what doesn’t, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts, leading to more effective campaigns and improved overall performance.
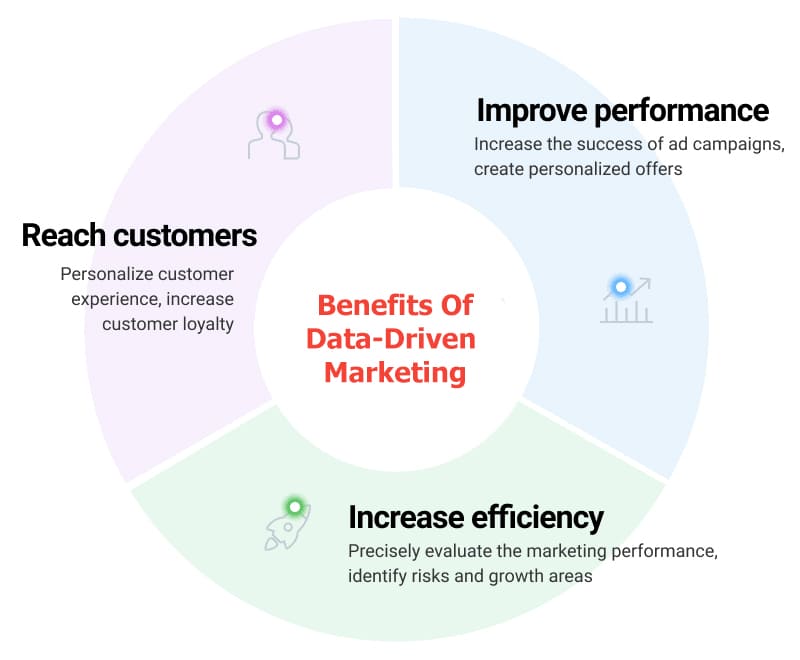
Leveraging a data-driven marketing approach has three main benefits:
- Precision in Customer Engagement: Target your audience with pinpoint accuracy, ensuring your messages resonate effectively.
- Increase Efficiency: Boost efficiency by leveraging insights, allowing for more effective resource allocation and streamlined processes.
- Elevated Performance Metrics: Witness a surge in overall performance as data-driven decisions optimize strategies, enhancing the impact of your marketing initiatives.
How is Data-Driven Marketing Different From Traditional Marketing?
The distinction between Data-Driven Marketing and Traditional Marketing lies in how they use information. Let’s take an example to understand this better.
Imagine you’re planning to sell a new type of shoe.
Traditional Marketing:
- Approach: In traditional marketing, you might put up posters around town or create a TV commercial to reach a large audience.
- Example: A billboard showing your new shoes to people passing by.
Data-Driven Marketing:
- Approach: In data-driven marketing, you would use information about people’s preferences to show your shoes specifically to those who are likely interested.
- Example: If someone often searches online for comfortable shoes, your shoe ad might pop up when they’re browsing the internet.
So, the headline is asking how marketing that uses data (like people’s online behaviour) to target specific groups is different from the more general and broad approach of traditional marketing (like putting up a billboard for everyone to see).
Traditional Marketing: Connecting with the Masses
Traditional marketing is the age-old method of promoting products or services to a large audience through various offline channels. Unlike the personalized and targeted approaches of modern digital marketing, traditional marketing employs tangible, conventional methods to reach the masses.

1. Print Marketing:
- Description: This involves using newspapers, magazines, brochures, and flyers to communicate messages about a product or service.
- Example: A full-page ad in a local newspaper featuring the latest fashion trends.
2. Broadcast Marketing:
- Description: Involves using television and radio to broadcast promotional messages.
- Example: A catchy jingle on the radio promoting a new fast-food deal.
3. Outdoor Marketing:
- Description: This includes billboards, posters, and banners placed in strategic locations for high visibility.
- Example: A billboard on a busy highway showcasing a new car model.
4. Direct Mail Marketing:
- Description: Sending physical promotional materials directly to the target audience’s mailbox.
- Example: A catalogue mailed to households featuring a range of kitchen appliances.
5. Telemarketing:
- Description: Involves making phone calls to potential customers to promote a product or service.
- Example: A call from a cable service provider offering a discounted subscription package.
Key Characteristics of Traditional Marketing
Mass Appeal: Traditional marketing relies on reaching a wide audience simultaneously. The goal is to cast a broad net and capture the attention of as many people as possible.
Tangible Presence: Materials used in traditional marketing, like print ads or billboards, have a physical presence. They exist in the real world and can be touched, seen, or heard without the need for a digital device.
One-Way Communication: Traditional marketing typically involves one-way communication, where the message is delivered from the business to the audience without immediate interaction. For example, a TV commercial presents information, but viewers don’t interact with the advertisement.
Challenges of Traditional Marketing

Limited Targeting: Traditional marketing methods lack the precision of digital strategies. They often reach a broad audience without specific targeting based on individual preferences or behaviours.
High Costs: Producing and distributing materials like TV ads or print brochures can be expensive. This can be a significant barrier for smaller businesses with limited budgets.
Limited Analytics: Tracking the success of traditional marketing campaigns is often more challenging. Unlike digital marketing, where analytics provide detailed insights, traditional methods may rely on estimations or surveys.
The Future of Traditional Marketing:
While digital marketing has gained prominence, traditional marketing remains relevant for certain audiences and industries. Some consumers still prefer tangible advertisements, and certain products or services may find success through traditional channels. However, the future likely involves a combination of both traditional and digital approaches, with businesses adapting their strategies to a changing landscape.
Unveiling the Power of Data-Driven Marketing: A Simple Guide
In the vast landscape of marketing, where businesses aim to grab attention and make an impact, a relatively new player has taken the spotlight—Data-Driven Marketing. But what exactly is it, and why is it creating such a buzz? Let’s break it down in simple terms.

Understanding the Basics: What is Data-Driven Marketing?
At its core, Data-Driven Marketing is a strategy that relies on insights and information derived from data to make informed decisions about how to approach and engage with customers. In simpler terms, it’s about using facts and figures to guide marketing efforts rather than relying solely on gut feelings or general assumptions.
Imagine you’re a shop owner and you want to sell a new line of sneakers. In a traditional approach, you might put up a big sign or run a TV ad hoping that a lot of people will see it.
In the world of Data-Driven Marketing, you would use information about people’s preferences and behaviours to show your new sneakers specifically to those who are most likely to be interested. It’s like tailoring your message to each individual customer, making your marketing efforts more efficient and effective.
Three Pillars of Data-Driven Marketing:
- Precision in Customer Engagement
- Example: If someone often searches online for running shoes, data-driven marketing can ensure they see ads for your new sneakers when they’re browsing the internet. It’s about reaching the right people at the right time with messages that matter to them.
- Streamlined Operations:
- Example: Let’s say your shop also sells hiking gear. With data-driven insights, you can allocate your resources more efficiently. If you notice that your online audience is more interested in running shoes than hiking boots, you can focus your marketing efforts and inventory accordingly.
- Elevated Performance Metrics:
- Example: By analyzing data on what customers respond to, you can continually refine your marketing strategies. If you find that customers engage more with video content than with written posts, you can adjust your approach to include more videos, thus improving the overall performance of your marketing efforts.
How Data-Driven Marketing Works
- Data Collection:
- Businesses collect data from various sources, such as website visits, social media interactions, and purchase history. This information provides valuable insights into customer behaviour.
- Analysis:
- The collected data is then analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and preferences. For example, if a significant number of customers tend to make purchases during specific times or after certain interactions, these patterns become crucial insights.
- Targeted Campaigns:
- Armed with these insights, businesses can create highly targeted and personalized marketing campaigns. This means that instead of sending the same message to everyone, they tailor messages to specific groups based on their preferences.
- Feedback Loop:
- The beauty of data-driven marketing is that it’s not a one-time effort. Marketers continually gather feedback on how their campaigns are performing. If certain strategies are proving more successful than others, adjustments can be made in real time for ongoing improvement.
The Benefits of Data-Driven Marketing
- Personalization:
- By understanding individual preferences, businesses can deliver personalized experiences, making their marketing messages more relevant and engaging.
- Efficiency:
- Resources are optimized as marketing efforts are directed toward audiences more likely to respond positively, eliminating wasted resources on broad campaigns with low relevance.
- Effectiveness:
- The ability to measure and analyze the performance of campaigns in real-time allows for quick adjustments, ensuring that marketing efforts are continually refined for maximum impact.
Data-driven marketing is like having a personal guide in the vast world of marketing. It’s about using information wisely to connect with customers in a way that feels tailored just for them.
By understanding their preferences and behaviours, businesses can create more meaningful interactions, making the marketing experience not only efficient but also enjoyable for both the business and the customer. It’s not just a strategy; it’s a journey towards making marketing work smarter, not harder.
Navigating the Challenges of Data-Driven Marketing: A Guide to Overcoming Hurdles
As businesses increasingly embrace the power of data-driven marketing to enhance their strategies, a new set of challenges arises. In this guide, we’ll explore the hurdles that come with data-driven marketing and provide insights on how to overcome them.
Challenge 1: Data Quality and Accuracy
Issue: The effectiveness of data-driven marketing heavily relies on the quality and accuracy of the data collected. Inaccurate or outdated information can lead to misguided decisions.
Solution: Regularly audit and clean your data. Implement validation processes to ensure the accuracy of incoming data. Invest in tools that can identify and rectify errors automatically.
Challenge 2: Privacy Concerns and Compliance
Issue: With increased scrutiny on data privacy, businesses must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and ensure compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA.
Solution: Prioritize transparency with customers about data usage. Implement robust consent mechanisms and stay informed about evolving privacy regulations. Regularly update privacy policies to align with current standards.
Challenge 3: Integration of Data Sources
Issue: Many businesses collect data from various sources, and integrating these disparate sources can be challenging, leading to fragmented insights.
Solution: Invest in integrated data platforms that can seamlessly merge data from different sources. Ensure that your data team is well-versed in data integration techniques.
Challenge 4: Talent Shortage in Data Analytics
Issue: The demand for skilled data analysts often outpaces the available talent pool, making it challenging for businesses to effectively analyze and interpret data.
Solution: Invest in training programs for existing staff or consider collaborations with external agencies. Leverage automated analytics tools to supplement human efforts.
Challenge 5: Balancing Personalization and Privacy
Issue: Customers value personalized experiences, but there’s a fine line between personalization and invading privacy. Striking the right balance is crucial.
Solution: Implement robust consent management systems. Allow customers to control the level of personalization they are comfortable with. Clearly communicate how data is used to enhance their experience.
Challenge 6: Overwhelming Amounts of Data
Issue: The abundance of data can be overwhelming, leading to analysis paralysis and decision-making delays.
Solution: Define clear objectives before collecting data. Focus on relevant metrics that align with business goals. Implement data visualization tools to simplify complex information.
Challenge 7: Aligning Data with Business Goals
Issue: Sometimes, there is a disconnect between the data collected and the overarching business objectives, leading to misaligned strategies.
Solution: Regularly revisit and reassess business goals. Ensure that the data collected directly contributes to these goals. Align data-driven insights with broader business strategies.
Challenge 8: Security Threats
Issue: As data becomes more valuable, it becomes a target for cyber threats. Ensuring the security of customer data is paramount.
Solution: Implement robust cybersecurity measures. Regularly update security protocols and educate employees on data security best practices.
Challenge 9: Rapidly Evolving Technology
Issue: The fast-paced evolution of technology can make it challenging for businesses to keep up with the latest tools and trends.
Solution: Stay informed about emerging technologies through continuous learning. Regularly reassess and update your technology stack to stay competitive.
Challenge 10: Measuring the Impact of Data-Driven Initiatives

Issue: Measuring the actual impact of data-driven initiatives on business outcomes can be complex.
Solution: Define clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) aligned with business objectives. Regularly assess and analyze the impact of data-driven strategies on these KPIs.
While data-driven marketing brings immense opportunities, businesses must proactively address these challenges to fully leverage the power of data. By implementing the suggested solutions, organizations can navigate the complexities and build a robust foundation for effective data-driven marketing strategies.
As technology continues to advance, data-driven marketing is positioned as a future-proof strategy. By embracing this approach, you align your marketing efforts with the evolving landscape of consumer expectations and technological capabilities. This forward-thinking mindset ensures that your marketing strategy remains relevant and effective in the long run.
In conclusion, the incorporation of data-driven marketing in your strategy is not just a choice; it’s a strategic imperative. The ability to harness the power of data provides unparalleled advantages in today’s competitive business environment. From precise targeting to measurable impact, data-driven marketing is the catalyst for unlocking success and ensuring your brand not only survives but thrives in the ever-evolving world of marketing.
A Layman’s Guide to Use Analytics For Your Marketing With Data
Imagine you’re the captain of a ship navigating through uncharted waters. Analytics in data-driven marketing is like having a reliable compass and a telescope – tools that not only guide you but also help you see beyond the horizon. Let’s break down how to use analytics for data-driven marketing in a way that’s as clear as the North Star.
1. Setting Your Course: Defining Objectives
Layman’s explanation: Before you embark on a journey, you need to decide where you want to go. Analytics helps you set your destination by defining clear objectives.
Example: Imagine you run an online store. Your objective might be to increase sales. Analytics would help you understand what steps on your website lead to more purchases.
2. Plotting Your Journey: Implementing Tracking Tools
Layman’s explanation: Once you know where you’re going, you need tools to track your progress. Analytics tools are like your ship’s navigation system, helping you see how close you are to your destination.
Example: In our online store example, you might use Google Analytics. It’s like a GPS for your website, showing you where your visitors come from, what they look at, and if they make a purchase.
3. Reading the Map: Analyzing Data
Layman’s explanation: As you sail, you need to read the map to make informed decisions. Analytics is your map, providing insights into what’s working and what needs adjustment.
Example: Analyzing data might reveal that more people buy when you offer free shipping. This insight becomes your map, showing you the route to increased sales.
4. Adapting to Storms: Making Real-Time Adjustments
Layman’s explanation: Storms (challenges) might come your way. Analytics helps you navigate by making real-time adjustments to your course.
Example: Imagine a sudden drop in website traffic. Analytics alerts you, allowing you to investigate and discover that a key webpage is down. You fix it, preventing potential lost sales.
5. Discovering Hidden Islands: Identifying Opportunities
Layman’s explanation: Sometimes, analytics reveals unexpected opportunities – hidden islands on your journey that you can explore for treasure.
Example: Through analytics, you find that many customers come to your website after seeing your social media posts. This insight becomes a new opportunity to invest more in social media marketing.
6. Measuring the Wind: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Layman’s explanation: Measuring the wind’s strength helps you gauge how fast you’re sailing. KPIs in analytics are like measuring the strength of your marketing efforts.
Example: If your objective is to increase brand awareness, a KPI could be the number of people who visit your website after seeing an online ad.
7. Keeping the Crew Happy: Customer Feedback
Layman’s explanation: Happy crew members make the journey smoother. Analytics includes feedback from customers, helping you understand their satisfaction.
Example: Customer reviews and comments on your website provide valuable feedback. If many customers mention they love a particular product, you can focus more on promoting it.
8. Arriving at Your Destination: Measuring Success
Layman’s explanation: Finally, when you reach your destination, you measure success. Analytics helps you see if you’ve achieved your objectives.
Example: If your goal was to increase sales, analytics shows you the increase in conversion rate or the number of purchases during your marketing campaign.
In essence, analytics in data-driven marketing is your trusty navigator, guiding your ship through the marketing seas. It’s not just about understanding the journey but also about making every adjustment and decision with confidence, ensuring a successful voyage towards your marketing goals. So, set sail with your analytics compass, and let the data-driven adventure begin!